POLYGON
Polygon is a plane figure bounded by many (usually five or more) straight lines.
When all the sides and included angles are equal, it is called as a REGULAR POLYGON.
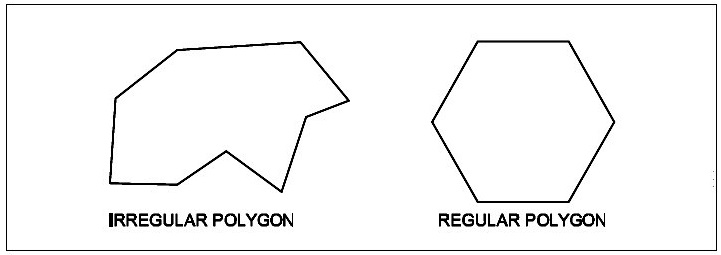
When all the sides and included angles are unequal, it is called IRREGULAR POLYGON.
Polygons are named in terms of their number of sides as given below:
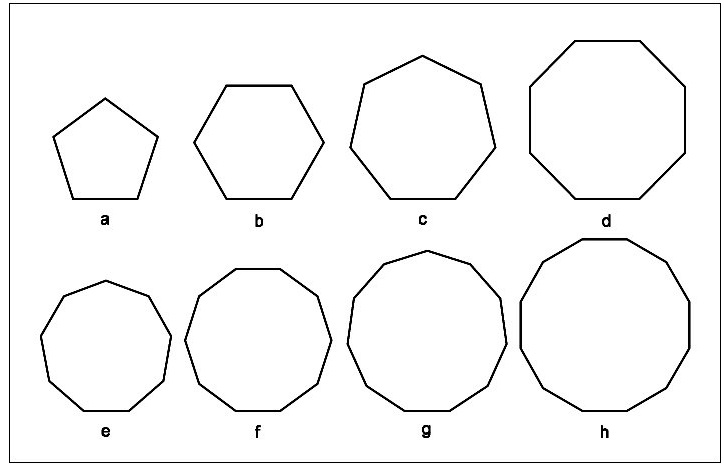
| S. No. | NAME | NUMBER OF SIDES |
| a | PENTAGON | 5 |
| b | HEXAGON | 6 |
| c | HEPTAGON | 7 |
| d | OCTAGON | 8 |
| e | NONAGON | 9 |
| f | DECAGON | 10 |
| g | UNDECAGON | 11 |
| h | DUODECAGON | 12 |
PROPERTIES OF POLYGON:
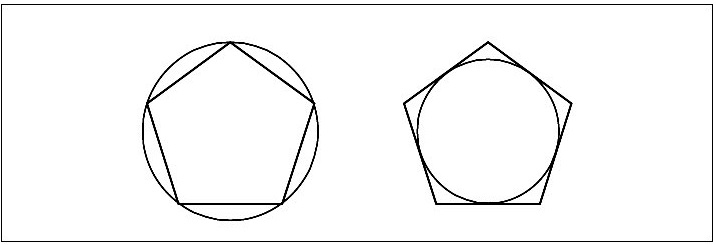
- All corners of a regular polygon lie on the circle. The sides of a regular polygon will be tangential to the circle drawn in side.
- The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is equal to (2 x n – 4) x right angle, where n is the number of sides.
- The sum of exterior angles of a polygon is equal to 360°.
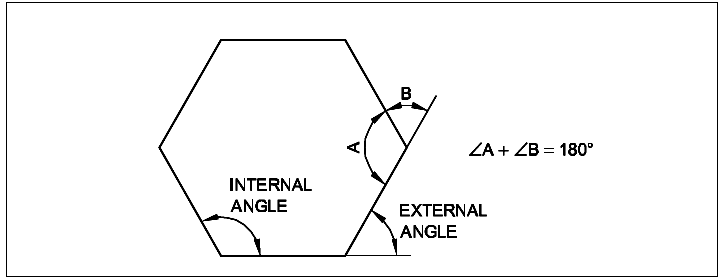
- The sum of the interior angle and the corresponding external angle is 180°.
Draw a regular heptagon of side 25 mm.
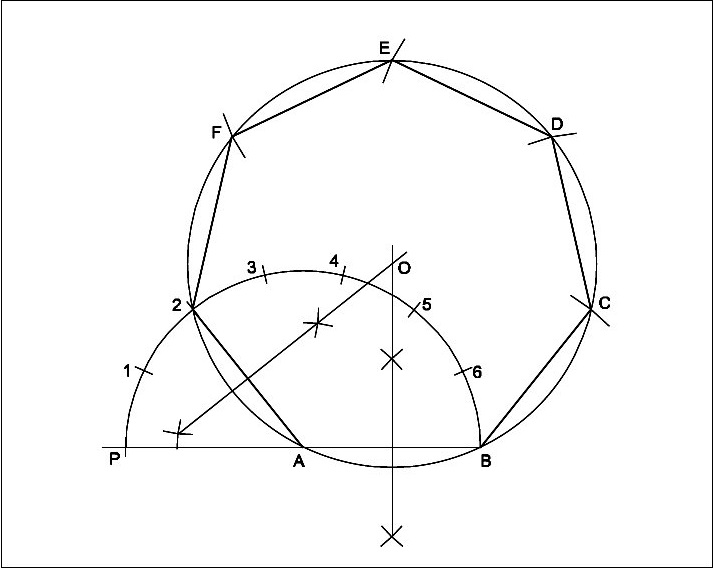
Semi-circular method
- Draw a line AB equal to 25 mm.
- Extend BA to a convenient length.
- `A’ as centre and radius AB describe a semi-circle.
- Divide the semi-circle into seven equal parts (number of sides) using divider.
- Number the points as 1,2,3,4,5,6 starting from `P’.
- Join A2
- Draw the perpendicular bisectors from 2A and AB intersecting at 0.
- `0′ as centre and OA or OB as radius describe a circle.
- Mark the points C,D,E,F and 2 on the circle such that BC = CD = DE = EF = F2 = AB.
- Join the line BC, CD, DE, EF and F2.
- ABCDEF2 is required heptagon.
Semi-circle method
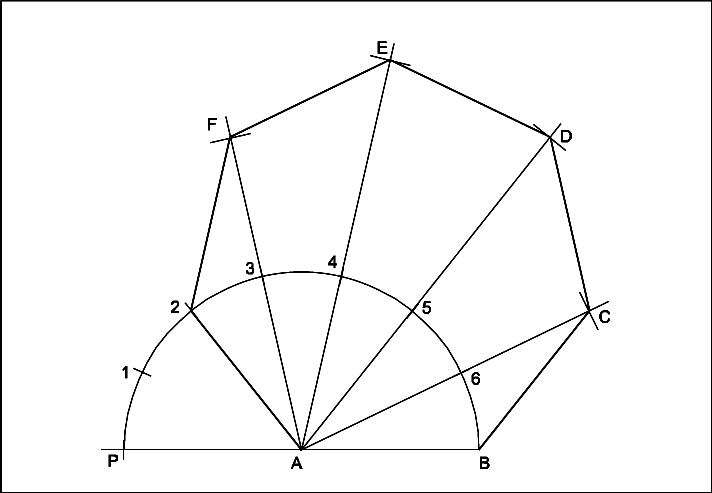
Follow the procedure upto dividing the semi-circle into number of equal parts.
- Join A2.
- Join A3, A4, A5 and A6 and extend to a convenient length.
- With centre `B’ and radius AB draw an arc cutting A6 extended line at `C’.
- `C’ as centre and same radius, draw an arc cutting the line A5 at `D’.
- Locate the points E & F in the same manner.
- Join BC, CD, DE, EF and F2.
- ABCDEF2 is the required heptagon.
Draw a Pentagon inside a circle of diameter 60 mm.
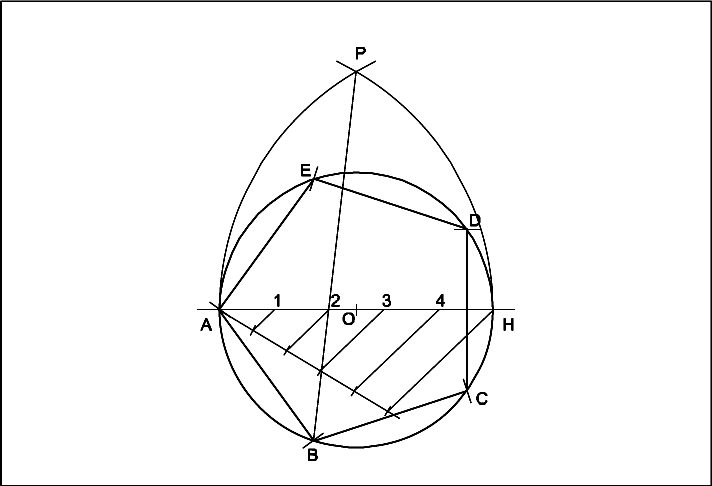
- Draw the line AH equals to 60 mm. (Diameter of circle).
- `O’ as centre OA as radius describe a circle.
- Divide AH into 5 equal parts (as many equal parts as the sides).
- A and H as centres, AH as radius describe arcs intersecting at `P’.
- Join P2 and extend it to meet the circle at `B’.
- Set off BC, CD, DE, EF equals to AB on the circle.
- Join the points.
- ABCDEF is the required pentagon.
Draw a Hexagon (Circumscribing) of side 32 mm by Arc Method.
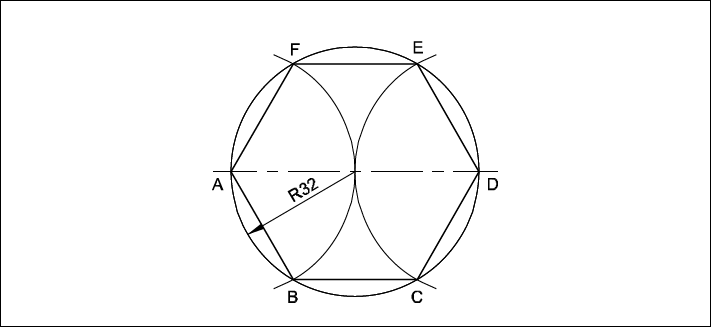
- Draw a circle of radius 32 mm.
- Mark the diameter AD.
- With same radius, A and D as centres. draw two arcs cutting the circle at points B,F,E & C respectively.
- Join AB, BC, CD, DE, EF and FA.
- ABCDE is the required hexagon.
Draw a Hexagon inside a circle of diameter 60 mm (inscribing).
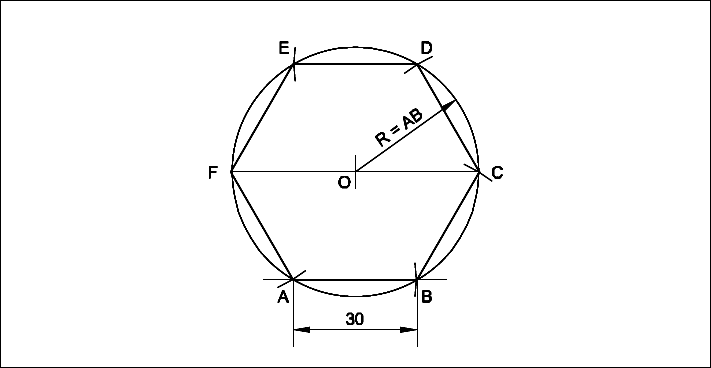
- Draw a line FC equal to 60 mm (Diameter of circle).
- ‘O’ as centre describe a circle on the diameter FC.
- F as centre FO as radius draw an arc at A.
- ‘A’ as centre, same radius draw an arc at B.
- In the same manner set the points C,D & E.
- Join AB, BC, CD, DE, EF and FA.
- ABCDEF is the required hexagon.
Draw a Hexagon with Across Flat Method.
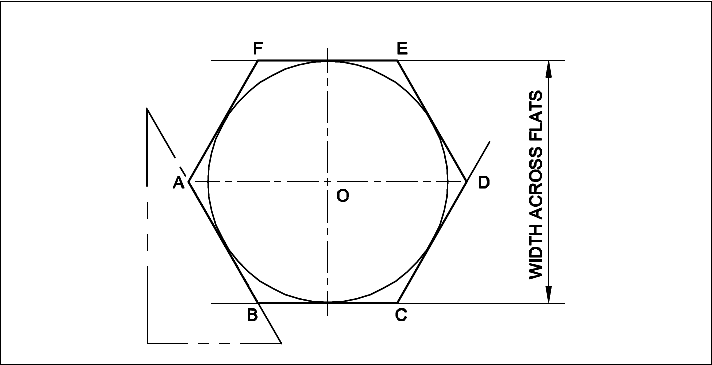
Hexagon, distance across flat of 45 mm
- Draw a circle of Φ 45. (45 mm is the size across flat).
- Draw two horizontal tangents BC and FE.
- With 60° setsquare draw four tangents, touching the horizontal tangents.
- Mark the corners A,B,C,D,E and F.
- ABCDEF is the required hexagon.
For More Previous Year Question Papers – CLICK HERE