OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Operations Management is concerned with the conversion of inputs into value added outputs using physical resources, so as to provide the desired utility to the customer while meeting the other organizational objectives of effectiveness.
TYPES OF BUSINESS OPERATIONS
- Manufacturing
- Services
- Trading
MANUFACTURING:
- The output of an operations system may be in terms of end product- physical goods such as automobiles, cement, paper, butter, books etc.
- raw materials are purchased and converted into a new final product for sales.
- Major business operations of manufacturing concerns are procurement, production and sales.
- The time required from procurement to sales will be relatively more for manufacturing organizations since the manufacture requires conversion time for processing the goods.
SERVICES:
- Output may be in terms of services such as in transportation, hospitals, educational institutions, banks, cinema halls etc.
- The major business process is to provide service at the point of consumption by the customers.
TRADING:
- Goods are purchased and sold without further processing.
- Major business process of trading are procurement and sale.
- Time required from procurement to sales will be relatively less for trading.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
The product life cycle is an important concept in manufacturing. It describes the stages a product goes through from when it was first thought of until it finally is removed from the market. Not all the products reach the final stage. Some continue to grow and others rise and fall.
MAIN STAGES OF THE PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
- INTRODUCTION– Researching, developing and then launching the product.
- GROWTH– When sales are increasing at their fastest rate.
- MATURITY- Sales are near their highest but the rate of growth is slowing down e.g. new competitors in the market or saturation.
- DECLINE- Final stage of the cycle when sales begin to fall.
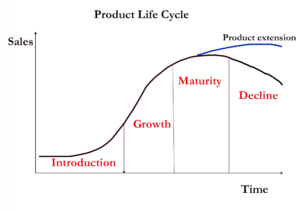
EXTENDING THE PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE:
Extension strategies extend the life of the product before it goes into decline. Various marketing techniques are used to improve the sales. Examples of the techniques are:
- ADVERTISING: Try to gain a new audience or remind the current audience.
- PRICE REDUCTION: More attractive to customers.
- ADDING VALUES: Add new features to the current product i.e. improving the specifications of a smartphone.
- EXPLORE NEW MARKETS: Selling the product into new geographical areas.
- NEW PACKAGING: Brightening up old packaging.
RELATED VIDEOS FOR OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:
For More Information- CLICK HERE
