OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
FORECASTING
- It is the first major activity in the planning. It involves careful study of past data and present scenario. The main purpose of forecasting is to estimate the occurrence timing or magnitude of future events.
- Once the reliable forecast for the demand is available, a good planning of activities is needed to meet the future demand.
Forecasting thus provides the input to the planning and scheduling process
Precise forecasting of economic activities, such as product demand is almost impossible because of many interactive factors, which are difficult to model. Despite the fact that highly reliable forecast is unrealistic, the approximate estimate forms the basis of planning process.
FEATURES OF FORECASTING:
- It is concerned with future events.
- It is necessary for planning process.
- The impact of future events has to be considered in the planning process.
- It is a guessing of future events.
- It considers all the factors which affect organizational functions.
- Personal observation also helps forecasting
PROCESS OF FORECASTING:
- Thorough Preparation of Foundation:
The very purpose of thorough preparation of a foundation is that the forecasting is based on the foundation.
- Estimation of Future:
The brightness of future period can be estimated in consultation with the key personnel & it may be communicated to all the employees of the business unit.
- Collection of Results:
Relevant records are prepared & maintained to collect the result.
- Comparison of Results:
The actual results are compared with estimated results to know deviations. This will help the management to estimate the future.
- Refining the Forecast:
The forecast can be refined in the light of deviations which seem to be more
FACTORS AFFECTING SALES:
- Reasonability of the business.
- Relative state of economy.
- Direct and indirect competition.
- Political Events.
- Style of fashions.
- Purchasing power.
- Population changes.
- Weather.
- Productivity changes.
IMPORTANCE OF FORECASTING
Good forecast of material , labor and other resources for operation are essentially needed by the managers. If good projection of future demand is available, the management may take suitable action regarding inventory. Similarly, if production activities are accurately forecasted, then balanced workload may be planned. Good labor relations may be maintained as there would be lesser hiring and firing activities by the management with better manpower planning.
ADVANTAGES:
- Effective handling of uncertainty.
- Better labor relations.
- Balanced workload.
- Minimization in the fluctuations of production.
- Better use of production facilities.
- Better material management.
- Better customer service.
- Better utilization of capital and resources.
- Better design of facilities and production system.
LIMITATIONS:
- Forecasting is to be made on the basis of certain assumptions and human judgments which yield wrong result.
- It can not be considered as a scientific method for guessing future events.
- It does not specify any concrete relationship between past and future events.
- It requires high degree of skill.
- It needs adequate reliable information so difficult to collect reliable information.
- Heavy cost and time consuming.
- It can not be applied to a long period
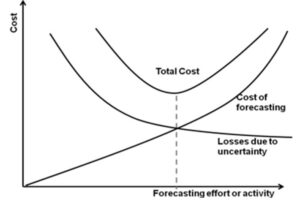
Efforts in forecasting activity involves two types of costs. While more effort in forecasting causes increased cost due to data collection and analysis; lesser forecasting activity involves lost revenue which may be due to unplanned labor, material, capital cost. Therefore a balance should be maintained in forecasting effort.
TYPES OF FORECASTING:
-
LONG RANGE FORECASTING
Consists of time period of more than 5 years
- Applications:
-
- Capital planning.
-
- Manpower planning.
-
- Estimating cash inflows.
-
- Determining dividend policy.
-
- Planning of long run production.
-
- Long run financial requirements.
-
- Budgetary control over expenditure.
-
- Plant location.
-
- Plant layout or expansion.
-
- New product planning.
-
- Research and development planning etc.
-
MEDIUM RANGE FORECASTING
Consists of time period of 1 to 5 years
- Applications:
-
- Sales planning and sales force decisions.
-
- Productions planning.
-
- Capital and cash planning.
-
- Inventory planning.
-
- Enrollment of students in a college etc.
-
SHORT RANGE FORECASTING
Consists of time period of one season, few months or few weeks.
- Applications:
-
- Purchasing.
-
- Formulation of suitable production policy.
-
- Regulate supply of raw material.
-
- Best utilization of machines.
-
- Regular availability of labor.
-
- Price policy formulation
-
- Setting the sales target.
-
- Overtime decisions.
-
- Scheduling of job.
-
- Machine maintenance etc.
RELATED VIDEOS:
